
The rudimental, indivisible steps are now named Actions (and not Activities).
#ACTIVITY DIAGRAMS DEFNATION VERIFICATION#
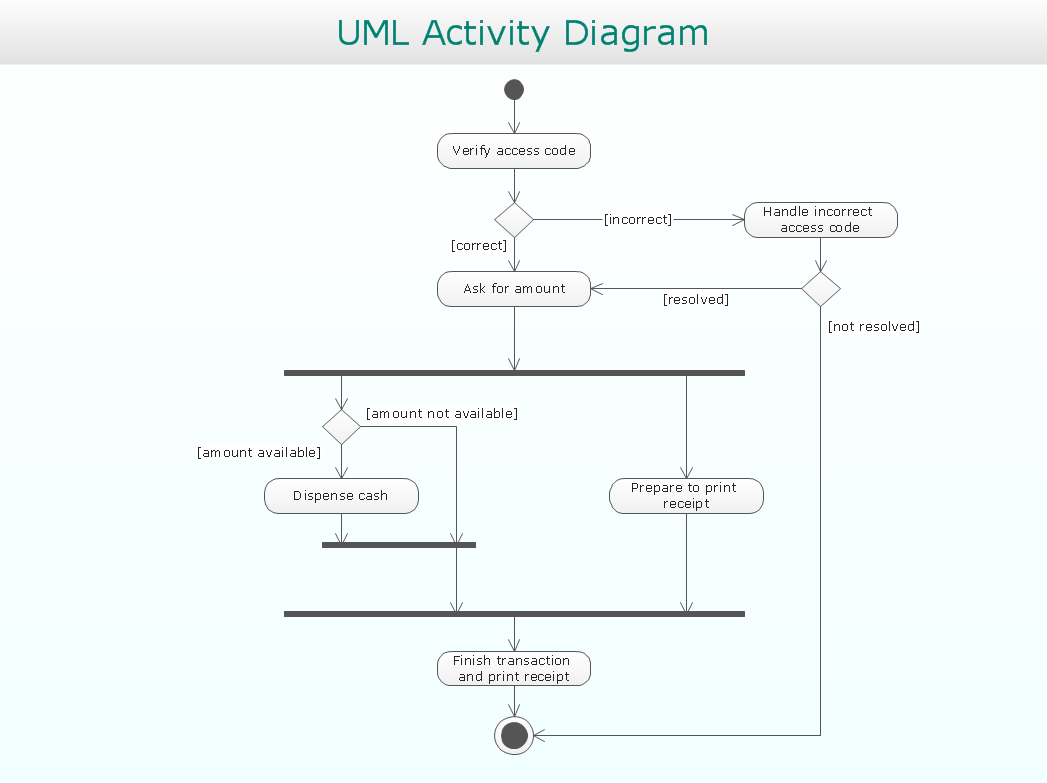
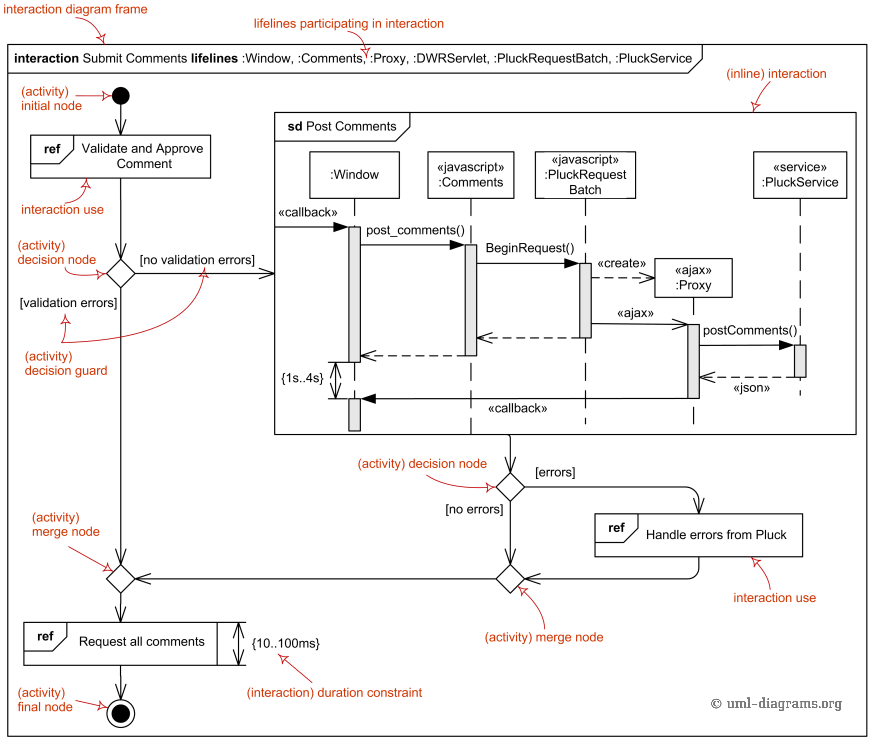
By this formal specification of the semantic of Activity-Diagrams it's possible to apply an automatic verification of Activity-Diagram, namely a simulation.ĭue to the revision, a change of terms is in effect: The token represents the progress of the logical flow or of the data-/object flow. A token corresponds to an executing thread, which can be generated and destroyed. Starting with UML 2.x the token semantics of Petri nets has been applied, providing precise rules for the logical flow and flow of objects, including parallelization, synchronization and merging of paths.
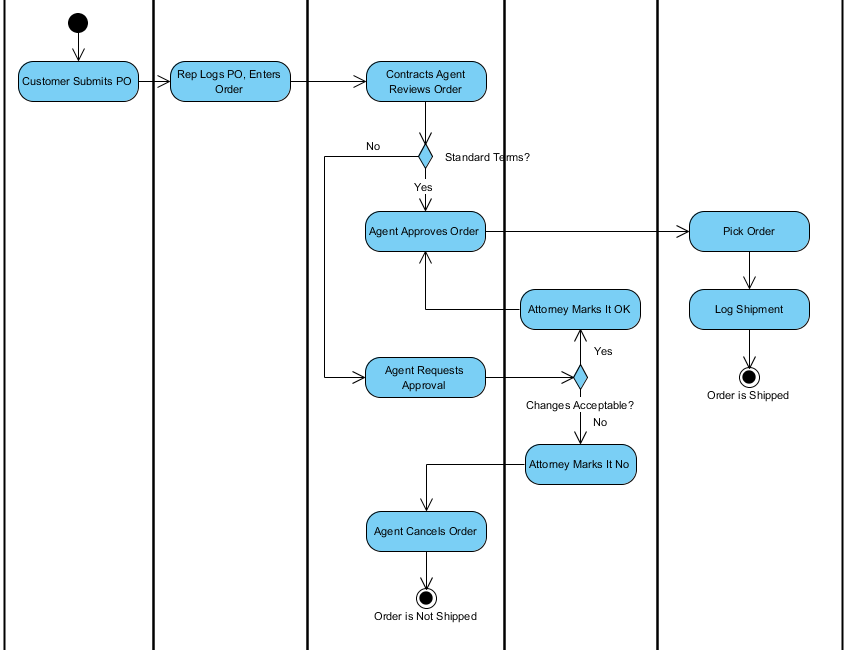
Up to UML 1.x Activity-Diagrams have been defined as a mixture of State-Diagrams, Petri nets and Process-Diagrams, leading to problems, practical and theoretical ones. They provide the entry and exit parameter values for the Actions. The small rectangles on the actions are so-called pins. This activity shows various kinds of nodes and edges. 17: Example of an Activity, "Production of Sixpacks" The precise declaration of activity parameters are at the top left directly under the name of the activity.įig. This activity has two parameters: an inbound parameter, produced bottles in the condition, and an outbound parameter, new sixpack. The following example shows an activity for the production of sixpacks.
These objects are placed on the Activity rectangle and also below the name of the Activity with type designations listed. Inbound or outbound objects in an Activity model are identified as parameters of that Activity. It's also correct to draw Activities within Activities - for better structuring.Īs with every behavior in UML, an Activity can also have parameters. There are several types of Actions available: normal (an atomic working step), CallBahaviourAction and CallOperationAction for referencing behavior defined somewhere else. Within an Activity you will find Actions. In the upper left corner is the name of the Activity. The Activity's nodes and edges are located within the rectangle. It is represented by a rectangle with rounded corners. A number of references to the UML versions can be found at the end of the chapter on Activity diagrams.Īctivity describes the procedural order of actions. In UML 1.x, the activity element yields to the action, whereas an entire activity model is now called Activity. The semantics of the individual model elements differs greatly from the model elements in UML 1.x despite the same terminology. In practice, it is now customary to cancel descriptions of scenarios expressly in diagrams in order to trace the contained expressions when covered during implementation, and to set up test cases. With Activity diagrams, however, it is possible to show even very complex processes with many exceptions, variations, branches and repetitions in a clear and coherent manner. Use cases can also be described with natural language, so-called scenarios, whereby the overview remains intact only for very simple processes.
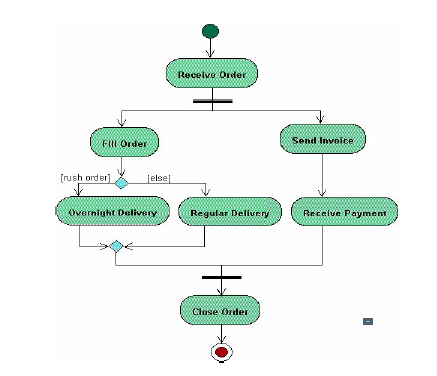
Single activities and their interdependencies are shown. Using Activity diagrams, chronological cycles can be graphically depicted as they are described in use cases.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
